カテゴリー: コンピュータ
-
三菱 CELP 方式音声コーデックの分析 (デコーダ・LSP パラメータ編)
三菱 CELP 方式音声コーデック (以下、M-CELP) は、デジタル MCA 無線や消防救急デジタル無線に用いられていることが知られる CELP 方式の音声コーデックです。このコーデックはプロプライエタリであり、消防救急デジタル無線に採用されるまではあまり知られていませんでした。消防救急デジタル無線は無線マニアによる聴取需要が大きいこともあり、5ch 上で解析を試みるコミュニティが形成され、結果的に匿名の人物による DSP エミュレータの開発に至りました。本記事では、このコーデックのデコード部におけるLSP パラメータの処理について分析します。
解析するバイナリ
本記事では、デジタル MCA 移動無線電話装置 EF-6190 に書き込まれている DSP 向けプログラム (Wup205r57) を解析するものとして話を進めます。
DSP
M-CELP は、原則として TMS320VC5416 という DSP に実装されることがわかっています。命令セットは TMS320C54x と呼ばれるものです。この逆コンパイルには Ghidra も対応していないので、解析するには逆アセンブリを読んで命令セットリファレンスと照らし合わせるほかありません。
エントリポイント
5ch 上の 549 氏によれば、エントリポイントはそれぞれ
- 初期化: 0x292AA
- エンコード: 0x39311
- デコード: 0x29365
です。今回はデコード部における LSP パラメータの処理が対象なので、0x29365 から処理をたどります。
ビットストリームの解析
ビットストリームの解析部は、0x2C975 (0x29365 -> 0x2EAF4 -> 0x2D352 -> 0x2C975) にあります。0x2C975 で解析されるビットストリームの形式は以下と思われます。(549 氏の分析も参考)
LSP パラメータ(合計 20 ビット):
- voiced_flag: 1 ビット
- main_index: 7 ビット
- sub_index_1: 6 ビット
- sub_index_2: 6 ビット
サブフレーム A(合計 31 ビット – 1, 3 番目のサブフレーム):
- pitch_delay: 8ビット
- fixed_codebook_index: 16ビット
- gain_code_book_index: 7ビット
サブフレーム B(合計 28 ビット – 2, 4 番目のサブフレーム):
- pitch_delay_delta: 5 ビット
- fixed_codebook_index: 16 ビット
- gain_code_book_index: 7 ビット
フレーム終端(合計 6 ビット):
- control_bit: 1 ビット
- 未使用: 5 ビット
フレーム全体のビット数: 143 ビット
ここで注目すべきなのは、LSP パラメータが有声・無声の別で異なる処理が行われると思われることと、コードブックが主・副で分かれていると思われることです。特に後者は、Split Vector Quantization (以下、SVQ) が行われていることを示しています。
LSP のデコード
解析されたビットストリームから LSP をデコードする処理は、0x2CE12 (0x29365 -> 0x2EAF4 -> 0x2D352 -> 0x2D14B -> 0x2D071 -> 0x2CE12) で行われています。ここで、0x2CE12 を Python で実装したコードを示します。
# func_ce12 def _generate_lsp_from_params(self, params: LspParameters): """ Generate LSP parameters from codebook indices. Args: params: LspParameters containing codebook indices and voiced flag """ # Get appropriate weights based on voiced flag is_voiced = params.voiced_flag == 1 base_weights, history_weights = self._get_weights(is_voiced, "generation") # Initialize LSP parameters lsp_params = np.zeros(self.ORDER, dtype=np.int16) # Get values from codebooks and convert to int16 main_codebook = np.array(LSP_MAIN_CODEBOOK, dtype=np.uint16).astype(np.int16) sub_codebook = np.array(LSP_SUB_CODEBOOK, dtype=np.uint16).astype(np.int16) main_value = main_codebook[params.main_index] sub_value_1 = sub_codebook[params.sub_index_1] sub_value_2 = sub_codebook[params.sub_index_2] # Combine main and sub values lsp_params[:5] = main_value[:5] + sub_value_1[:5] lsp_params[5:] = main_value[5:] + sub_value_2[5:] # Apply spacing adjustments # ar0 = 10, ar2 = 0x0060 self._enforce_minimum_lsp_separation(lsp_params, 10) # ar0 = 5, ar2 = 0x0060 self._enforce_minimum_lsp_separation(lsp_params, 5) # Apply smoothing filter # ar1 = 0x7BEC, ar2 = 0x0060, ar3 = 0xF205, ar4 = 0x6C8A, ar5 = 0xF1C9 self._current_lsp_params = self._apply_smoothing_filter( lsp_params, base_weights, self._lsp_history, history_weights ) # Update history with new parameters # ar2 = 0x0060, ar3 = 0x6C8A self._update_history(lsp_params) # Stabilize and store results # ar2 = 0x7BEC self._enforce_lsp_stability_constraints(self._current_lsp_params)SVQ のデコードは極めて簡単で、各コードブックから参照した値を前後半に分けて加算しているだけです。その後、LSP 間の最小距離を確保して安定性を高め、過去の LSP の履歴をもとに LSP の変化を緩やかにしています。最後に、最小値と最大値のクリッピングを行い、再び LSP 間の最小距離を確保して安定性を高めています。LSP の変化の平滑化では、有声・無声の別によってフィルタ重みを調整して様子もあります。
総括
商用の CELP 方式音声コーデックである M-CELP を分析し、計算複雑性の低減やデコードされた音声の品質の向上の方法がわかりました。
付録
M-CELP のデコーダの一部を Python で実装したコードを付録とします。
from typing import Literal import numpy as np from numpy.typing import NDArray from .frame import Frame, LspParameters from .lsp_constants import ( LSP_MAIN_CODEBOOK, LSP_SUB_CODEBOOK, LSP_UNVOICED_HISTORY_WEIGHTS, LSP_VOICED_HISTORY_WEIGHTS, LSP_UNVOICED_BASE_WEIGHTS, LSP_VOICED_BASE_WEIGHTS, LSP_UNVOICED_PREDICTION_WEIGHTS, LSP_VOICED_PREDICTION_WEIGHTS, LSP_COSINE_LOOKUP_TABLE, LSP_SINE_LOOKUP_TABLE, ) class Mcelp: # LSP configuration constants ORDER = 10 # Number of LSP coefficients per frame # LSP stability constraint constants MIN_LSP_VALUE = 0x29 # Minimum value for first LSP MAX_LSP_VALUE = 0x6452 # Maximum value for last LSP MIN_LSP_SPACING = 0x141 # Minimum spacing between adjacent LSPs # LSP frequency domain transformation constants LSP_SCALING = 0x517D # Initial scaling factor MAX_TABLE_INDEX = 0x3F # Maximum lookup table index (63) # Default LSP values for initialization # fmt: off _DEFAULT_LSP_PARAMS = np.array( [0x0924, 0x1247, 0x1B6B, 0x248F, 0x2DB2, 0x36D6, 0x3FF9, 0x491D, 0x5241, 0x5B64], dtype=np.uint16 ).astype(np.int16) _DEFAULT_FREQUENCY_DOMAIN_LSP_PARAMS = np.array( [0x7AD1, 0x6BB0, 0x53D4, 0x352C, 0x1237, 0xEDC9, 0xCAD4, 0xAC2C, 0x9450, 0x852F], dtype=np.uint16 ).astype(np.int16) # fmt: on def __init__(self) -> None: """Initialize MCELP with default state.""" self._reset_state() def _reset_state(self) -> None: """Reset internal state to default values.""" # 0x6C8A self._lsp_history = np.stack([self._DEFAULT_LSP_PARAMS] * 3) # 0x7BEC self._current_lsp_params = self._DEFAULT_LSP_PARAMS.copy() # 0x6CB2 self._latest_lsp_params = self._DEFAULT_LSP_PARAMS.copy() # 0x6F34 self._current_frequency_domain_lsp_params = ( self._DEFAULT_FREQUENCY_DOMAIN_LSP_PARAMS.copy() ) # 0x6CBC self._latest_frequency_domain_lsp_params = ( self._DEFAULT_FREQUENCY_DOMAIN_LSP_PARAMS.copy() ) self._voiced_flag = False def _get_weights( self, voiced_flag: bool, weight_type: Literal["generation", "prediction"] ) -> tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]: """ Get appropriate weights based on voice flag and weight type. Args: voiced_flag: True if frame is voiced, False otherwise weight_type: Type of weights to retrieve ("generation" or "prediction") Returns: Tuple of (base_weights, history_weights) """ # Select the appropriate base weights based on weight type and voiced flag if weight_type == "generation": base_weights_source = ( LSP_VOICED_BASE_WEIGHTS if voiced_flag else LSP_UNVOICED_BASE_WEIGHTS ) else: # prediction base_weights_source = ( LSP_VOICED_PREDICTION_WEIGHTS if voiced_flag else LSP_UNVOICED_PREDICTION_WEIGHTS ) # Convert base weights to int16 base_weights = np.array(base_weights_source, dtype=np.uint16).astype(np.int16) # Get history weights (same for both generation and prediction) history_weights_source = ( LSP_VOICED_HISTORY_WEIGHTS if voiced_flag else LSP_UNVOICED_HISTORY_WEIGHTS ) history_weights = np.array(history_weights_source, dtype=np.uint16).astype( np.int16 ) return base_weights, history_weights # func_ca35 def _enforce_minimum_lsp_separation( self, lsp_params: NDArray[np.int16], # ar2 threshold: int, # ar0 ) -> None: """ Enforce minimum separation between adjacent LSP parameters. Args: lsp_params: Array of LSP parameters to adjust threshold: Minimum separation threshold """ for i in range(self.ORDER - 1): # Calculate difference between current and next parameter difference = lsp_params[i] - lsp_params[i + 1] adjusted_difference = difference + threshold # If parameters are too close, adjust them equally in opposite directions if adjusted_difference > 0: half_adjustment = adjusted_difference >> 1 lsp_params[i] -= half_adjustment lsp_params[i + 1] += half_adjustment # func_c960 def _apply_smoothing_filter( self, current_values: NDArray[np.int16], # ar2 current_weights: NDArray[np.int16], # ar3 history_values: NDArray[np.int16], # ar4 history_weights: NDArray[np.int16], # ar5 ) -> NDArray[np.int16]: # ar1 """ Apply smoothing filter to LSP parameters using weighted history. Args: current_values: Current LSP parameters current_weights: Weights for current parameters history_values: Historical LSP parameters history_weights: Weights for historical parameters Returns: Filtered LSP parameters """ # Convert to int64 to prevent overflow during calculations current_values = current_values.astype(np.int64) current_weights = current_weights.astype(np.int64) history_values = history_values.astype(np.int64) history_weights = history_weights.astype(np.int64) filtered_values = np.zeros(self.ORDER, dtype=np.uint16) for i in range(self.ORDER): accumulator = current_values[i] * current_weights[i] for j in range(3): # Process 3 frames of history accumulator += history_values[j][i] * history_weights[j][i] # Scale down by 2^15 filtered_values[i] = accumulator >> 15 return filtered_values.astype(np.int16) # func_c941 def _predict_lsp_with_feedback( self, current_values: NDArray[np.int16], # ar1 current_weights: NDArray[np.int16], # ar4 history_values: NDArray[np.int16], # ar2 history_weights: NDArray[np.int16], # ar3 ) -> NDArray[np.int16]: # ar5 """ Predict LSP parameters with feedback mechanism. Args: current_values: Current LSP parameters current_weights: Weights for current parameters history_values: Historical LSP parameters history_weights: Weights for historical parameters Returns: Predicted LSP parameters """ # Convert to int64 to prevent overflow during calculations current_values = current_values.astype(np.int64) current_weights = current_weights.astype(np.int64) history_values = history_values.astype(np.int64) history_weights = history_weights.astype(np.int64) predicted_values = np.zeros(self.ORDER, dtype=np.uint16) feedback = 0 for i in range(self.ORDER): base = current_values[i] << 16 for j in range(3): # Process 3 frames of history base -= (history_values[j][i] * history_weights[j][i]) << 1 intermediate = base & 0xFFFF base -= feedback feedback += (current_weights[i] * intermediate) << 1 feedback >>= 16 feedback += (current_weights[i] * (base >> 16)) << 1 predicted_values[i] = feedback >> 13 return predicted_values.astype(np.int16) # func_c9ce def _enforce_lsp_stability_constraints( self, lsp_params: NDArray[np.int16], # ar2 ) -> None: """ Enforce stability constraints on LSP parameters: 1. Ensure monotonic increase 2. Apply minimum/maximum value constraints 3. Ensure minimum spacing Args: lsp_params: LSP parameters to stabilize """ # Step 1: Single pass to ensure monotonic increase for i in range(len(lsp_params) - 1): if lsp_params[i] > lsp_params[i + 1]: # Swap adjacent LSPs if out of order lsp_params[i], lsp_params[i + 1] = lsp_params[i + 1], lsp_params[i] # Step 2: Apply minimum value constraint to first LSP lsp_params[0] = max(lsp_params[0], self.MIN_LSP_VALUE) # Step 3: Ensure minimum spacing between adjacent LSPs # Uses original values as reference to prevent cascading shifts for i in range(len(lsp_params) - 1): min_next_value = lsp_params[i] + self.MIN_LSP_SPACING if lsp_params[i + 1] < min_next_value: lsp_params[i + 1] = min_next_value # Step 4: Apply maximum value constraint to last LSP lsp_params[-1] = min(lsp_params[-1], self.MAX_LSP_VALUE) # func_c7ee def _transform_lsp_to_frequency_domain( self, lsp_params: NDArray[np.int16] # ar2 ) -> NDArray[np.int16]: # ar3 """ Transform LSP parameters from line-pair domain to frequency domain. Args: lsp_params: LSP parameters to transform Returns: Transformed frequency domain parameters """ # Convert lookup tables to int64 to prevent overflow cos_table = ( np.array(LSP_COSINE_LOOKUP_TABLE, dtype=np.uint16) .astype(np.int16) .astype(np.int64) ) sin_table = ( np.array(LSP_SINE_LOOKUP_TABLE, dtype=np.uint16) .astype(np.int16) .astype(np.int64) ) scaled_values = np.zeros(self.ORDER, dtype=np.uint16) lsp_params = lsp_params.astype(np.uint64) for i in range(self.ORDER): # Initial scaling initial_product = (lsp_params[i] * self.LSP_SCALING) << 1 # Calculate lookup table index and interpolation fraction table_index = initial_product >> 8 table_index = min(table_index, self.MAX_TABLE_INDEX << 16) >> 16 fraction = ((initial_product >> 16) & 0xFF) << 3 # Linear interpolation between lookup table values base_value = cos_table[table_index] << 16 scale_factor = sin_table[table_index] interpolation = (scale_factor * fraction).astype(np.int64) << 1 scaled_values[i] = (base_value + interpolation).astype(np.int64) >> 16 return scaled_values.astype(np.int16) # func_c9c2 def _update_history( self, lsp_params: NDArray[np.int16], # ar2 ) -> None: """ Update LSP parameter history by shifting and inserting new parameters. Args: lsp_params: New LSP parameters to add to history """ # Shift history array and insert new parameters at index 0 # self._lsp_history: ar3 self._lsp_history = np.roll(self._lsp_history, 1, axis=0) self._lsp_history[0] = lsp_params.copy() # func_ce12 def _generate_lsp_from_params(self, params: LspParameters): """ Generate LSP parameters from codebook indices. Args: params: LspParameters containing codebook indices and voiced flag """ # Get appropriate weights based on voiced flag is_voiced = params.voiced_flag == 1 base_weights, history_weights = self._get_weights(is_voiced, "generation") # Initialize LSP parameters lsp_params = np.zeros(self.ORDER, dtype=np.int16) # Get values from codebooks and convert to int16 main_codebook = np.array(LSP_MAIN_CODEBOOK, dtype=np.uint16).astype(np.int16) sub_codebook = np.array(LSP_SUB_CODEBOOK, dtype=np.uint16).astype(np.int16) main_value = main_codebook[params.main_index] sub_value_1 = sub_codebook[params.sub_index_1] sub_value_2 = sub_codebook[params.sub_index_2] # Combine main and sub values lsp_params[:5] = main_value[:5] + sub_value_1[:5] lsp_params[5:] = main_value[5:] + sub_value_2[5:] # Apply spacing adjustments # ar0 = 10, ar2 = 0x0060 self._enforce_minimum_lsp_separation(lsp_params, 10) # ar0 = 5, ar2 = 0x0060 self._enforce_minimum_lsp_separation(lsp_params, 5) # Apply smoothing filter # ar1 = 0x7BEC, ar2 = 0x0060, ar3 = 0xF205, ar4 = 0x6C8A, ar5 = 0xF1C9 self._current_lsp_params = self._apply_smoothing_filter( lsp_params, base_weights, self._lsp_history, history_weights ) # Update history with new parameters # ar2 = 0x0060, ar3 = 0x6C8A self._update_history(lsp_params) # Stabilize and store results # ar2 = 0x7BEC self._enforce_lsp_stability_constraints(self._current_lsp_params) # func_d071 Part 1 def _generate_lsp_from_codebook(self, params: LspParameters) -> None: """ Generate new LSP parameters from codebook indices. Args: params: LspParameters containing codebook indices and voiced flag """ # ar1 = 0x7BEC, ar7 = 0x6C8A self._generate_lsp_from_params(params) # ar3(0x7BEC) -> ar2(0x6CB2) self._latest_lsp_params = self._current_lsp_params.copy() self._voiced_flag = params.voiced_flag == 1 # func_d071 Part 2 def _predict_lsp_parameters(self) -> None: """ Predict LSP parameters based on history and current state. """ # Get appropriate weights based on voiced flag base_weights, history_weights = self._get_weights( self._voiced_flag, "prediction" ) # Copy latest parameters to current # ar2(0x6CB2) -> ar3(0x7BEC) self._current_lsp_params = self._latest_lsp_params.copy() # Calculate predicted parameters # ar1 = 0x6CB2, ar2 = 0x6C8A, ar3 = 0xF1E7, ar4 = 0xF223, ar5 = 0x7BE2 predicted_lsp_params = self._predict_lsp_with_feedback( self._latest_lsp_params, base_weights, self._lsp_history, history_weights, ) # Update history with predicted parameters # ar2 = 0x7BE2, ar3 = 0x6C8A self._update_history(predicted_lsp_params) # func_d071 def process_frame(self, frame: Frame) -> np.ndarray: """ Process a frame of speech data to generate or predict LSP parameters. Args: frame: Frame containing control bit and LSP parameters Returns: Frequency domain LSP parameters """ if frame.control_bit == 0: # Generate new LSP from codebook self._generate_lsp_from_codebook(frame.lsp_params) else: # Predict LSP based on history self._predict_lsp_parameters() # Transform to frequency domain # ar2 = 0x7BEC, ar3 = 0x6F34 self._current_frequency_domain_lsp_params = ( self._transform_lsp_to_frequency_domain(self._latest_lsp_params) ) return self._current_frequency_domain_lsp_params -
なぜ DAM Multi Dimensional Sound は優れていないのか
DAM Multi Dimensional Sound (以下、MDS) とは、第一興商製商用カラオケ機器 LIVE DAM WAO! (型番: DAM-XG9000; 以下、XG9) に採用される新たな演奏方式です。詳細は以下の記事に譲ります。
簡単に言えば、従来の同社機種は搭載しているハードウェア MIDI 音源で楽曲を演奏していましたが、この機種では事前に録音した音声データを収録しそのまま再生するということです。この方式が従来の方式に比べて優れていない理由を説明します。
従来方式 A (通常/MIDI + ADPCM 方式)
従来の通常の方式は、MIDI と呼ばれる楽譜のような情報をもとに、MIDI 音源という電子楽器が事前にサンプリングされた楽器等の音を再生して楽曲を演奏していました。また、これだけでは表現できない音 (バックコーラス等) を再生するために、ADPCM とばれる別の音声データを再生する機能もありました。
従来方式 B (生音/MP3 方式)
従来の生音と呼ばれる方式は、実際の楽器で演奏した音声を MP3 に収録し、そのまま再生することにより楽曲を演奏していました。
MDS (Opus + ADPCM 方式)
MDS は、音声データ Opus (MP3 のようなもの) と ADPCM を併せて再生して楽曲を演奏する方式です。技術的詳細は以下の記事に譲ります。
音質の問題
MDS は結局の所、一部の楽曲で従来方式 A (通常) の録音を用いているだけということがわかっています。この方式では、テンポやキーを変更する操作 (タイムストレッチ・トランスポーズ) を行うと音質が悪化してしまうという欠点が現れてしまいます。この点、従来の MIDI 音源であれば克服することが可能でした。なお、従来方式 B (生音) ではこの欠点が同様に現れます。
容量の問題
ほとんどの楽曲で採用されている従来方式 A (通常) の場合、カラオケ機器のディスク容量を専有するデータの多くが MIDI ファイル (実際には OKD 方式) です。MIDI ファイルは、音声そのものではなく音声を再生するのに必要な演奏情報を含んでいるのみであり、楽譜のようなものであるため、多くの場合数十から数百 kB の容量で収まっていました。しかし、音声そのものを含む MDS の場合、10 MB を超えることが珍しくありません。音質が改善するわけでもなく、ただデータの容量だけが肥大しているのです。
どうしてこうなったのか
匿名の有識者は
XG9 が脱 MIDIしてるの、CRI が自社依存率を上げて脱YAMAHA 方向に営業しているとかな気もする
と推測します。CRI とは、株式会社CRI・ミドルウェアのことで、LIVE DAM Ai (型番: DAM-XG8000; 以下、XG8) から採点ゲームなど機器の一部のソフトウェアを開発しています。一方、YAMAHA は遅くとも BB Cyber DAM (型番: DAM-G100; 以下、G100)の頃から DAM シリーズの開発に関わっています。
2025-03-13 追記
この推測を裏付けるのが libMultiTrackPlayer4.so 内のテンポ・キー変更操作に関するコードです。このコード内では、関数 criKspKeyTempoController_ProcessInterlevedInt16 が呼ばれています。この関数は、libcri_ksp_key_tempo_controller.so の中にあり、CRI が開発したライブラリにテンポ・キー変更操作が依存していることがわかります。
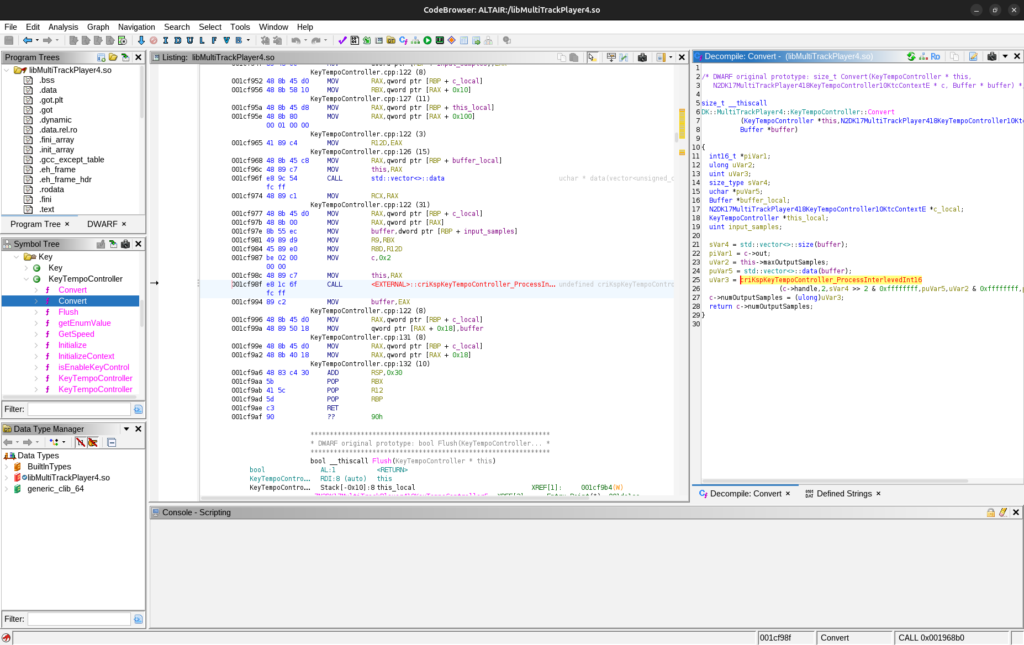
libMultiTrackPlayer4.so 内で関数 criKspKeyTempoController_ProcessInterlevedInt16 が呼ばれている様子 -
DAM Multi Dimensional Sound の正体
DAM Multi Dimensional Sound (以下、MDS) とは、第一興商製商用カラオケ機器 LIVE DAM WAO! (型番: DAM-XG9000; 以下、XG9) に採用される新たな演奏方式です。技術的詳細は以下の記事に譲ります。
簡単に言えば、従来の同社機種は搭載しているハードウェア MIDI 音源で楽曲を演奏していましたが、この機種では事前に録音した音声データを収録しそのまま再生するということです。
「これまでにない臨場感あふれるサウンド」とは何か
プレスリリースによれば
従来の音源技術を見直し、新たに「DAM Multi Dimensional Sound」へと進化させました。最新のソフトウェアシンセサイザーや生演奏を組み合わせたハイブリッド演奏方式を採用することで、使用できる音源に制約がなくなり、これまでにない臨場感あふれるサウンドを実現します。
従来のMIDI音源方式に加えて、最新のソフトウェアシンセサイザーやプロミュージシャンの生演奏を組み合わせたハイブリッド演奏方式を採用。高音質かつ重厚なサウンドが楽しめます。
などとされています。従来の同社機種の演奏方式よりも優れた音質になったかのような表現がされていることがわかります。そこで、実際に従来の機種による演奏と MDS とでは音声がどのように異なるかを検証しました。
音声波形の比較
わかりやすく、LIVE DAM Ai (型番: DAM-XG8000; 以下、XG8) に由来する従来のハードウェア MIDI 音源による出力を録音した音声 (以下、音声 A) と MDS 方式のファイルから抽出した音声 (以下、音声 B) の波形を比較します。今回注目する部分は、to the beginning – Kalafina (DAM 楽曲情報) の 56.82 秒付近、パーカッションのみが演奏される部分です。これらの波形を示します。
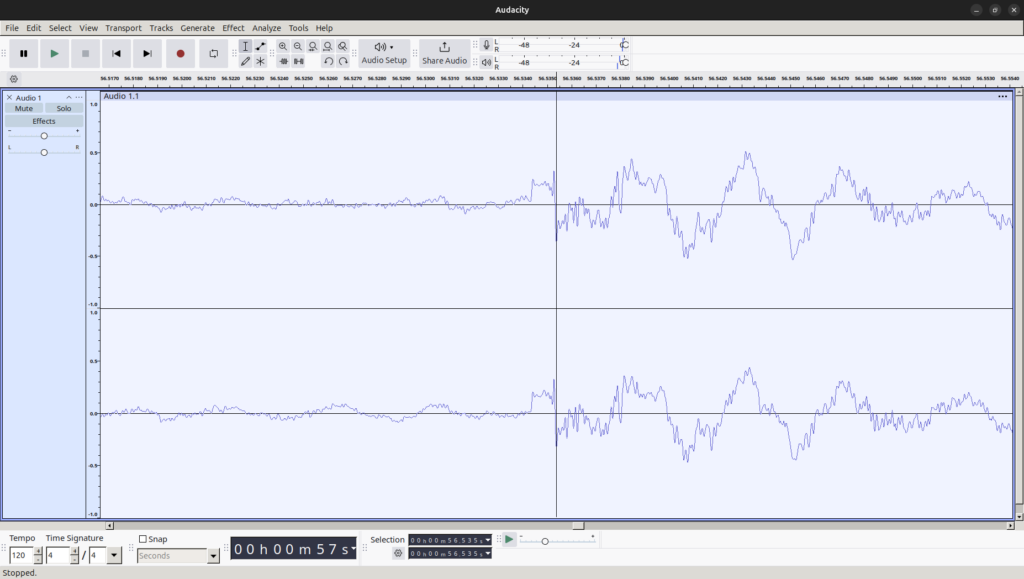
音声 A の波形 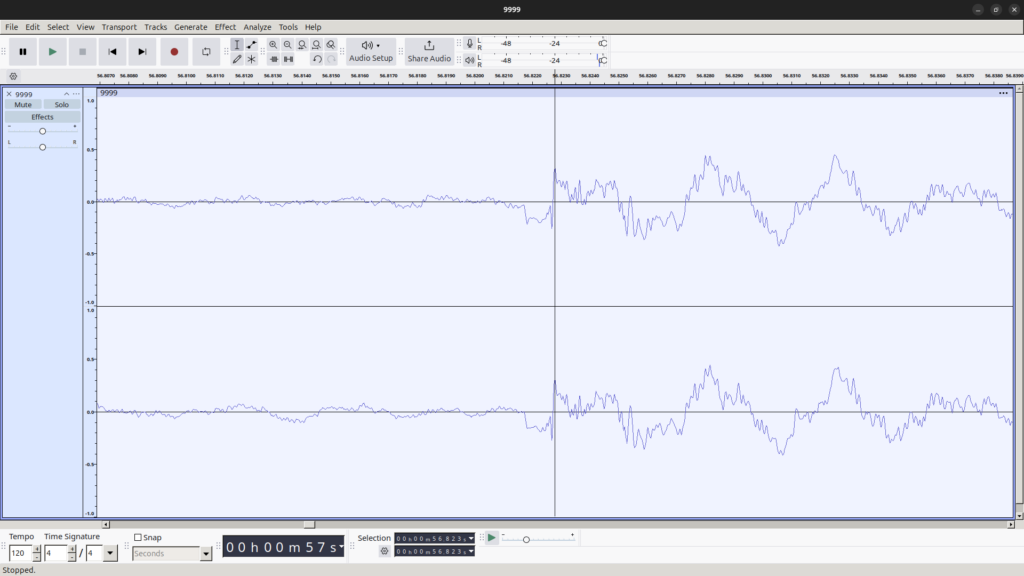
音声 B の波形 これらを一見してわかることは、おおよその形、特に楽器の鳴り始めの部分が似ていることです。一方、位相は逆であるように見えます。ここで、両者の画像を重ね合わせ、さらに位相やスケールをできるだけ一致するように上下反転、拡大縮小した画像を示します。
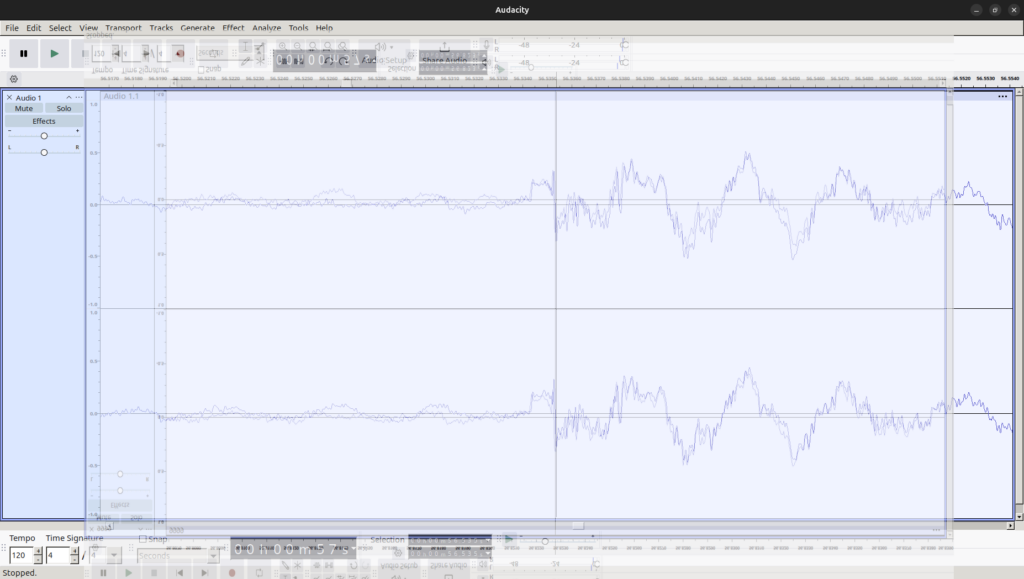
それぞれの波形が概ね一致することがわかります。
結論
音声 A の録音時の音量、発声タイミングやフィルタ処理の微妙な違い等を考慮すると、音声 A と音声 B はほぼ同一のものであると言えます。言い換えれば、MDS の音声には従来のハードウェア MIDI 音源による出力を録音した音声も含まれているということであり、少なくとも今回検証した楽曲においては、従来の演奏方式よりも優れた音質の音声が出力されるということはないようです。
-
LIVE DAM WAO! の分析
LIVE DAM WAO! (型番: DAM-XG9000; 以下、XG9)は、第一興商製の商用カラオケ機器です。

LIVE DAM WAO! (右から 2 番目) 及び周辺機器; プレスリリースより 旧機種からの主な変更点は、以下とされます。(プレスリリースより抜粋)
- DAM Multi Dimensional Sound
- 歌うまフィルター
- なりきりエフェクト
- ハモルン
- 精密採点Ai Heart
分析手法
今回の分析では、システムログとソフトウェアのバイナリを入手し、これらを利用しました。なお、これらは適法に取得されたものです。
ハードウェアアーキテクチャ
今回分析した XG9 (シリアル番号: BA0NNNNN;以下、対象 XG9) の主なハードウェアアーキテクチャは、以下です。
- マザーボード: Advantech HVS-1030K
- CPU: 12th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i3-12100E (4 コア 8 スレッド; 3.2 GHz)
- RAM: 16 GB
- SSD: SM659GX8 CDZ (8 GB)
- HDD: 任意の 12 TB モデル x2
ソフトウェアアーキテクチャ
対象 XG9 の主なソフトウェアアーキテクチャは、以下です。
- OS: Poky Linux 11.3.0
- カーネル: Linux 5.15.49-intel-pk-standard
- メインプログラム名: altair
DAM Multi Dimensional Sound
この記事では、従来の MIDI 音源に代わるとされる DAM Multi Dimensional Sound について掘り下げます。これはプレスリリースにおいて
従来のMIDI音源方式に加えて、最新のソフトウェアシンセサイザーやプロミュージシャンの生演奏を組み合わせたハイブリッド演奏方式を採用。高音質かつ重厚なサウンドが楽しめます。
と説明されています。
ヤマハ製音声入出力ボード YBD
一世代前の機種である LIVE DAM Ai (型番: DAM-XG8000; 以下、XG8)までは、YAMAHA が開発したカラオケ機器向け音源ボード (音声入出力ボード) YBD シリーズが搭載されていました。

Advantech 製マザーボード HVS-1010K (左) と YAMAHA 製音源ボード YBD3 (右); XG8 カタログより XG9 において、YBD がどうなったかをソフトウェアから考察します。XG8 と XG9 には、それぞれ SphinxManager (XG8)、SphinxManager2 (XG9) というソフトウェアが搭載されています。SphinxManager(2) は、両機種に搭載された音声入出力デバイスを制御するためのものです。XG8 の SphinxManager には、USB 接続された MIDI デバイスを制御するためのコードが含まれていました。しかし、XG9 の SphinxManager2 には、それが含まれていません。他のソフトウェアを探しても、そのような部分は見つかりませんでした。つまり、XG9 の音声入出力ボードには、MIDI 音源は搭載されていないと結論付けられます。(搭載されているが使用されないという可能性は一旦考えないものとします。)
MTF 形式
従来の MIDI 方式で用いられていた楽曲演奏情報ファイル OKD 形式 (関連: 同人誌, GitHub リポジトリ) の代替となる楽曲音声ファイル が MTF 形式です。MTF 形式の実体は gzip で圧縮されたアーカイブファイルであり、展開すると以下のようなファイルが現れます。
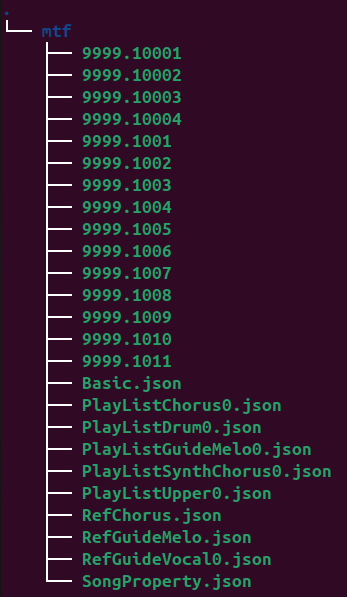
各ファイルの内容は、以下です。
- 9999.1000[1-4]: パーカッション, その他, ガイドメロディ,シンセサイザコーラス (OPUS)
- 9999.10NN: バックコーラス (ADPCM)
- *.json: メタデータ等
他、AutoVocalEffect.mid というファイルが含まれる場合があり、新機能のなりきりエフェクトの制御で使用されるようです。なりきりエフェクトはプレスリリースで
原曲でアーティストが使用している特殊なボイスエフェクトを再現。対象のパートのときだけ拡声器になったり、機械音声のエフェクトがかかるなど、ライブや原曲の雰囲気に近づけることができます。
と説明されています。
総括
LIVE DAM WAO! は、商用カラオケ機としては珍しく MIDI 音源を搭載しないことを選択した機種です。このような機種が誕生した理由は主に
- インターネット回線の広帯域化
- HDD の高容量化
であると考えます。XG9 と第一興商との間を結ぶ回線は 100 Mbps から 1 Gbps の帯域幅を持ちますし、XG9 は 12 TB の HDD を 2 台搭載しています。従来、MIDI ファイルは小さな情報量で幅広い表現力を持つ演奏情報ファイルとして利用され、演奏されるときには演奏機械で MIDI を解釈し音声を生成していました。しかし、演奏機械に転送し、保存される情報の量の制限が緩和され、このような方式を用いなくて良いと判断されたのでしょう。この判断の良し悪しの評価は行いませんが、カラオケ機器の新しい形が生まれたといえます。
-
プログラミング言語 Ruby の馴染めない点
私は昨年、 Ruby を用いて Web サービスを開発するという業務に少しだけ従事しました。
そこで初めて Ruby というプログラミング言語について基本的な事項を知ることになったのですが、これがどうも私にはしっくりこないものであったので、関係する事実とその感想等を述べたいと思います。関数呼び出しの括弧を省略する記法がある
多くのプログラミング言語では、f という名の関数を呼び出すとき
f() f(arg1) f(arg1, arg2)などとしますが、Ruby においてはリファレンスマニュアルの該当項目にある通り、括弧を省略した
f f arg1 f arg1 arg2のような記法が許されています。
x = aなどと記述されると、x に変数 a の値が代入されるのか、あるいは関数 a を呼び出した返り値が代入されるのか視覚的にわかりません。
これは、非常に混乱する記法であるからやめるべきだと思いました。if 文と逆の役割をする構文がある
リファレンスマニュアルの該当項目にある通り、if 文と逆の役割をする unless 文があります。
unless error_detected p "Hello, world!" # 正常時ここに到達する end私にはこの構文の必要性が理解できません。
if !error_detected p "Hello, world!" # 正常時ここに到達する endではいけないのでしょうか。
同義の組み込み関数が別名で複数ある
String::size(), String::length() などがこれに該当します。
混ぜて使うと混乱するため、どちらかだけで良いのではないでしょうか。&&, || の式が真偽値以外を返す
JavaScript などにも似た仕様がありますが、リファレンスマニュアルの該当項目 には
&& 演算子について
左辺を評価し、結果が偽であった場合はその値(つまり nil か false) を返します。左辺の評価結果が真であった場合には右辺を評価しその結果を返します。
あるいは || 演算子について
左辺を評価し、結果が真であった場合にはその値を返します。左辺の評価結果が偽であった場合には右辺を評価しその評価結果を返します。
とあり
nil && false && 1 && 0 # nil nil || false || 1 || 0 # 1のようになります。
また、nil と false の評価は同じ偽であるのに
nil || false = nil false || nil = falseとなり、これも直感的に理解すると記述を誤る可能性がある記法であるからやめるべきだと思いました。
&&, ||, ! 演算子と and, or, not 演算子がある
and は同じ働きをする優先順位の低い演算子です。
あるいは
or は同じ働きをする優先順位の低い演算子です。
などとあります。なぜ同じ役割を持つ論理演算子が異なる優先順位で複数存在しているのかが理解できません。
not 演算子に至っては、! 演算子と全く同じです。
明らかに混ぜて使うと混乱するため、どちらかだけで良いのではないでしょうか。独特な命名慣習
自らのオブジェクトや引数に取ったオブジェクトに破壊的な影響を及ぼすなど、「呼び出しに注意を要する」関数には f! などと末尾に感嘆符を付して命名するといものの、
「呼び出しに注意を要する」というのが具体的にどのような基準であるのか明文化されていません。また、真偽値を返す関数には f? などと末尾に疑問符を付して命名するそうです。これは明解ではありますが、なぜ真偽値を返す関数だけ特別扱いなのでしょうか。
総括
以上に述べた点は、私の主観にはしっくりこないものでした。
そのような記法を忌避すれば良いのではないかという意見があるかと思いますが、どうも Ruby のプログラマは私が違和感を感じる記法であっても積極的に用いるようです。
ソフトウェアの開発は必ずしも一人で行うものではないため、私一人が特定の記法を忌避するというのは難しいです。